What is Server Monitoring?
Server monitoring is a critical aspect of maintaining and optimizing server performance. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Server Monitoring, its importance, and best practices.
Today’s digital world depends so much on internet services and applications that server performance is essential to guaranteeing a smooth user experience. Servers are hardware (or more often now applications) that handle and store data that is requested by other devices, software, or users. Hundreds or perhaps thousands of requests may be handled concurrently by a single server. Therefore, a crucial component of IT infrastructure management is making sure that every server in an organization is functioning as it should.
Server monitoring is a critical aspect of maintaining and optimizing server performance, ensuring that servers can handle the expected load and operate efficiently. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of server monitoring, its importance, and best practices.
What is Server Monitoring?
The procedure of constantly examining and evaluating server performance indicators to guarantee that the server is operating effectively and smoothly is known as server monitoring. It involves monitoring several metrics, including response times, network traffic, disk I/O, CPU, and memory utilization. Server monitoring tools collect, store, and analyze this data, providing valuable insights into the server’s health and performance.
We here at Cloudphant offer you a fully productive dashboard from where you can easily monitor all this, and more very easily and take measures to guarantee optimal performance of your servers. This makes us the go-to choice of WordPress websites to host their servers.
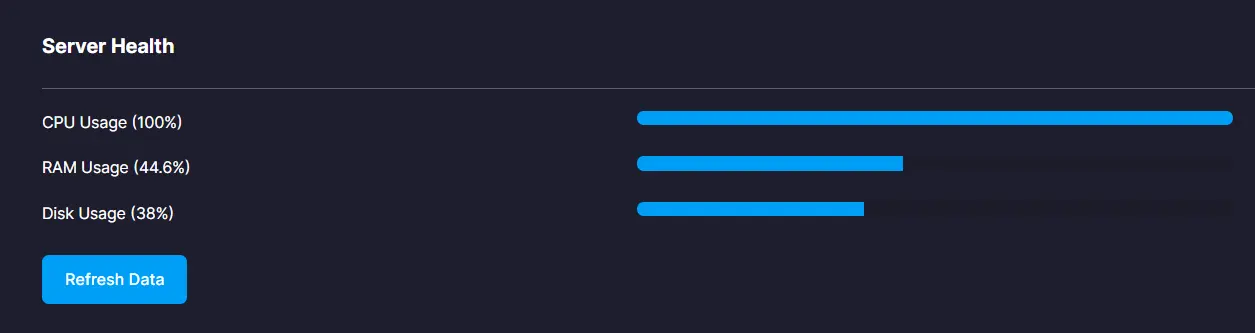
Importance of Server Monitoring:
- Identifying Performance Issues: Server monitoring helps in identifying performance bottlenecks and issues such as high CPU usage, memory leaks, or network congestion. Early detection allows for timely resolution, minimizing downtime, and ensuring uninterrupted service.
- Optimizing Resource Utilization: Administrators can find and distribute underused resources more effectively by keeping an eye on server performance indicators. This improvement lowers expenses and enhances server performance generally.
- Capacity Planning: Server monitoring provides insights into the server’s capacity and performance limits. This information is crucial for capacity planning, ensuring that the server can handle expected loads without performance degradation.
- Proactive Maintenance: By monitoring, possible problems may be recognized and fixed before they become serious ones. Reliability and stability of the server environment are maintained in part by this proactive strategy.
- Enhancing User Experience: Slow-loading websites or applications often leads to frustrated end users, who may leave and never return. Being proactive helps you provide a faster, smoother experience for customers. By ensuring optimal server performance, businesses can provide a better user experience, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Enhanced Security: Monitoring server performance is crucial for detecting any abnormal patterns or activities that could potentially signal security breaches or attempted attacks. Ensuring the security of customer data and maintaining trust requires the detection and identification of potential cyber threats.
Difference Between Server Monitoring and Server Performance Monitoring:
Although tracking and evaluating server metrics is a component of both server monitoring and server performance monitoring, there are several significant differences between the two:
Server Monitoring:
Server monitoring is a broad term that refers to the overall process of observing and managing a server’s health and availability. It involves monitoring various aspects of the server, such as:
- Availability: Checking if the server is up and running.
- Resource Usage: Monitoring CPU, memory, disk space, and network usage.
- Service Health: Ensuring that critical services are running smoothly.
- Security: Monitoring for any unauthorized access or potential security breaches.
- Logs and Events: Keeping track of system logs and events for troubleshooting and auditing purposes.
Server monitoring is more focused on ensuring the server’s basic functionality and availability rather than its performance under load.
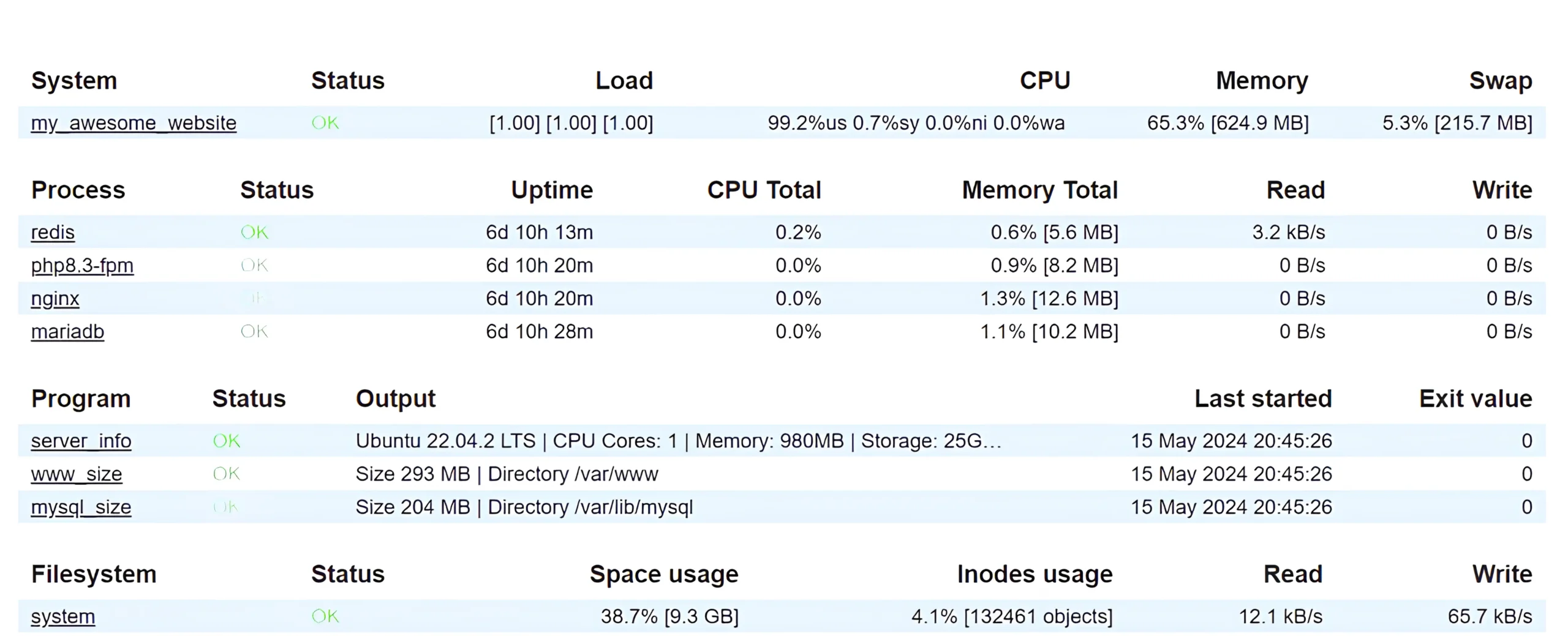
Server Performance Monitoring:
On the other hand, server performance monitoring is a subset of server monitoring that specifically focuses on tracking and analyzing server performance metrics. It involves monitoring metrics such as:
- CPU Usage: The percentage of CPU resources being utilized.
- Memory Usage: The amount of memory being used by the server.
- Disk I/O: Input/output operations per second on the disk.
- Network Traffic: The amount of data being sent and received over the network.
- Response Times: The time taken for the server to respond to requests.
Server performance monitoring is more concerned with how well the server is performing under various conditions and loads. It helps in identifying performance bottlenecks, optimizing resource usage, and improving overall server efficiency.
Key Differences:
- Scope: Server monitoring is broader in scope, covering the overall health and availability of the server, while server performance monitoring is more focused on performance metrics.
- Objective: The goal of server performance monitoring is to maximize server performance and efficiency; the goal of server monitoring is to make sure the server is up and running and that its services are available.
- Metrics: Server monitoring includes availability, resource usage, and security metrics, while server performance monitoring focuses on performance-related metrics such as CPU, memory, disk I/O, and network usage.
Although, Server monitoring is essential for ensuring the basic functionality and availability of a server, server performance monitoring is crucial for optimizing server performance and efficiency under various conditions and loads. Both types of monitoring are important components of a comprehensive server management strategy.
How to Monitor Server Performance?
Monitoring server performance involves the following steps:
Step 1: Selecting the Right Monitoring Tools: There are various server monitoring tools available, ranging from open-source to commercial solutions. It’s important to choose a tool that meets your specific requirements in terms of features, scalability, and ease of use. Some popular server monitoring tools include Nagios, Zabbix, Prometheus, and Datadog.
Step 2: Defining Key Performance Metrics: Identify the key performance metrics that are relevant to your server environment. These metrics typically include CPU usage, memory usage, disk I/O, network traffic, and response times. These metrics will serve as the basis for monitoring and analysis.
Step 3: Setting up Monitoring Agents: Install monitoring agents on the servers to collect performance data. These agents periodically send the data to the monitoring tool for analysis. The agents should be lightweight and efficient to minimize resource overhead on the server.
Step 4: Configuring Alerts: Set up alerts based on predefined thresholds for key performance metrics. Alerts notify administrators of any issues or anomalies, allowing for timely action. Alerts can be configured to be sent via email, SMS, or through the monitoring tool’s dashboard.
Step 5: Analyzing Performance Data: Regularly analyze the performance data collected by the monitoring tool to identify trends, patterns, and potential issues. Use this analysis to optimize server performance and address any underlying problems. Most monitoring tools provide dashboards and reports to help visualize and analyze performance data.
Step 6: Capacity Planning: Use the performance data to forecast future resource requirements and plan for capacity upgrades or optimizations accordingly. By understanding the server’s capacity and performance limits, you can ensure that it can handle expected loads without performance degradation.
Step 7: Implementing Continuous Monitoring: Server performance can vary over time due to changes in the server environment or workload. Implementing continuous monitoring ensures that you can quickly identify and address any performance issues that arise. Regularly review and adjust monitoring thresholds and configurations as needed.
Step 8: Integrating with Other Systems: Consider integrating your server monitoring tool with other systems such as IT ticketing systems, configuration management tools, and automation frameworks. This integration can help streamline processes and improve overall efficiency in managing server performance.
Best Practices for Server Performance Monitoring:
- Establish Performance Baselines: Determine the normal operating parameters for your servers by establishing performance baselines during periods of typical workloads. This will help identify deviations from expected behavior and facilitate proactive troubleshooting.
- Define Monitoring Thresholds: Set appropriate thresholds for critical performance metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk space. These thresholds should trigger alerts when exceeded, enabling prompt investigation and remediation.
- Implement Alerting and Notification Systems: Configure alerting mechanisms to notify the appropriate personnel or teams when performance issues or outages occur. Effective alerting systems ensure timely response and mitigation efforts.
- Correlate Data from Multiple Sources: Integrate data from various monitoring sources, including system logs, application logs, and network monitoring tools. Correlating data from multiple sources can provide a comprehensive view of system performance and aid in root cause analysis.
- Automate Monitoring and Reporting: Leverage automation tools to streamline monitoring processes, such as data collection, analysis, and reporting. Automated monitoring reduces the risk of human error and ensures consistent and timely monitoring.
- Regularly Review and Optimize: Regularly review monitoring configurations, thresholds, and alerts to ensure they align with evolving business requirements and changing workloads. Optimize monitoring strategies based on historical data and lessons learned.
- Implement Capacity Planning: Utilize historical performance data and trend analysis to anticipate future resource requirements and plan for capacity adjustments or hardware upgrades in advance.
- Foster Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Encourage collaboration and knowledge sharing among IT teams, developers, and stakeholders. Regular communication and cross-functional understanding can lead to more effective monitoring strategies and faster issue resolution.
End Note:
Establishing an efficient and dependable server environment requires server performance monitoring. Strong monitoring techniques allow companies to reduce downtime, proactively spot and fix possible problems, and maintain a high service standard for their users or clients. Continuously monitoring server performance, adhering to best practices, and leveraging the right tools and techniques are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and delivering exceptional digital experiences.
Recent Post
Mastering Load Balancing for Optimal WordPress…
Enhance your WordPress site's performance and reliability…
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): A Comprehensive Guide
Discover the ins and outs of Cross-Site…
Understanding Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Explore Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): how they…




